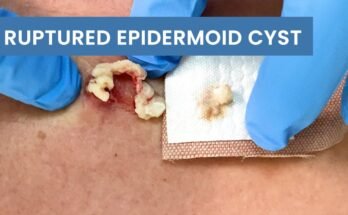
An infected cyst on the shoulder can cause discomfort, swelling, redness, and pain due to the accumulation of pus and inflammation. Proper drainage is necessary to relieve symptoms, promote healing, and prevent complications. This guide covers the procedure for draining an infected cyst, aftercare, and precautions to avoid recurrence.
Understanding an Infected Cyst
A cyst is a closed sac filled with fluid, pus, or other materials that can develop under the skin. When a cyst becomes infected, bacteria multiply within it, leading to inflammation, tenderness, and sometimes fever. Infected cysts should not be popped at home as improper drainage can lead to further infection or abscess formation. Medical professionals typically perform the drainage under sterile conditions.
Indications for Drainage
Drainage of an infected cyst is recommended if:
- The cyst is painful, swollen, and red.
- There is a visible accumulation of pus.
- The infection is causing discomfort or limiting movement.
- The cyst has ruptured but has not completely drained.
- There is a risk of the infection spreading.
Step-by-Step Drainage Procedure
1. Preparation and Sterilization
A healthcare professional will follow these steps:
- The affected area is cleaned with an antiseptic solution to reduce infection risk.
- Local anesthesia (lidocaine) may be injected to numb the area and minimize pain.
- Sterile gloves, surgical instruments, and gauze are prepared for the procedure.
2. Incision and Drainage
- A small incision is made in the cyst using a sterile scalpel.
- The pus and infected material are gently expressed from the cyst.
- The inside of the cyst may be flushed with saline solution to remove any remaining debris and bacteria.
- If necessary, a small drainage tube or packing gauze may be placed inside the cyst to allow further drainage over the next few days.
3. Dressing and Bandaging
- The wound is covered with a sterile dressing to protect it from further contamination.
- Instructions on how to change the dressing and keep the area clean are given.
Post-Procedure Care
1. Wound Care
- Keep the area clean and dry. Change the dressing as instructed.
- Wash hands before touching the wound to prevent reinfection.
- Avoid excessive movement of the shoulder to promote healing.
2. Medication
- Antibiotics may be prescribed to prevent further infection.
- Pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can be taken to manage discomfort.
3. Follow-Up
- The patient may need to return to the doctor for dressing changes or removal of any packing material.
- If the cyst was large or deeply infected, further medical intervention may be required.
Precautions and When to Seek Medical Help
Seek medical attention if:
- The wound becomes increasingly painful, swollen, or red.
- Pus continues to drain for an extended period.
- Fever or chills develop, indicating systemic infection.
- The cyst recurs frequently.
Prevention of Recurrence
- Maintain good hygiene and keep the skin clean.
- Avoid squeezing or popping cysts at home.
- If cysts frequently form, consult a doctor about potential underlying causes, such as skin conditions or genetic factors.
Properly draining an infected cyst on the shoulder under medical supervision ensures safe and effective healing. Following post-procedure care instructions minimizes complications and helps prevent recurrence.